Google Desktop....The most exciting new feature launched by Google Labs. A set of tools making computer navigation easy as never before. It includes a desktop navigation tool, or simply a search box, that searches you computer for the item that you ask for. And plus, if it is not there on you computer, you can directly dowmload that object without any searching! It even gives you Google Gadgets, which display instant info on any topic that you ask for, and that too, on your desktop!
Here are a few of its features-
Sidebar
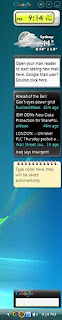
The main new feature of Google Desktop is the sidebar, for Windows only (although Google is planning on adding this feature to Linux). The side bar consists of several gadgets which display information. The Sidebar comes pre-installed with the following gadgets:
* Email - a panel which lets one view one's Gmail messages.
* Scratch Pad - here one can store random notes; they are saved automatically
* Photos - displays a slideshow of photos from the "My Pictures" folder (address can be changed)
* News - shows the latest headlines from Google News, and how long ago they were written. The News panel is personalized depending on the type of news you read.
* Weather - shows the current weather for a location specified by the user.
* Web Clips - shows recent posts from your favorite RSS feeds.
* Google Talk - If you have Google Talk installed, double clicking the window title will dock it to one's sidebar.
When minimized, the sidebar will become either a Deskbar, or a Floating Deskbar, depending on which one was displayed last. The default is a floating Deskbar. To minimize the sidebar, click on the horizontal line in the top-right hand corner of the sidebar. Like the Windows Taskbar, the GDS sidebar can be set to Auto-Hide mode, where it will only appear once the user moves his or her mouse towards the side where it resides. If not on auto-hide, by default the sidebar will always take up about 1/6 - 1/9 of one's screen (depending on screen resolution), and other windows are forced to resized. However, the sidebar can be resized to take less space, and you can disable the "always on top" feature in the options. With the auto-hide feature on, the sidebar temporarily overlaps your maximised window.
Additional gadgets can be downloaded from the Gadgets & Plug-ins[2] gallery, or by clicking "Add Gadgets", which shows a gallery, allowing the user to browse both installed gadgets and the other available gadgets.
All gadgets can be moved and reordered. Several options are also available for some gadgets.
Another feature that comes with the sidebar is alerts. When the Sidebar is minimized, new e-mail and news can be displayed on a pop-up window above your Windows Task Bar. This is configurable via the main sidebar menu, accessible by clicking on the arrow in the top-right of the sidebar.
Quick Find
When searching in the sidebar, deskbar or floating deskbar, Google Desktop displays a "Quick Find" window. This window is filled with 6 (number can be changed) most relevant results from your computer, results which change as you type, so you can get to what you want on your computer without having to open another browser window.
Deskbars
Deskbars are not a new feature to Google Desktop. They are a box which enables one to type in your search query directly from one's desktop. Web results will open in a browser window, and selected computer results will be displayed in the "Quick Find" box. A Deskbar can either be a fixed deskbar, which sits in your Windows Taskbar, or a Floating Deskbar, which one may position anywhere one wants on one's desktop.
Gadgets & Plug-ins
Desktop gadgets are interactive mini-applications that can be placed anywhere on the user's desktop to show new email, weather, photos and personalized news. Other gadgets include a clock, calendar, scratch pad, todo list and more. You can find gadgets made by Google, as well as third-party ones, at the Gadgets & Plug-ins gallery.
Google offers an SDK for people who wish to write plug-ins for Google Desktop: it's called the Google Desktop SDK. These plug-ins can increase the functionality of the program, such as allowing for indexing of more file types or addition of panels to the sidebar. Besides the main official blog, Inside Google Desktop, another blog, Google Desktop APIs blog, has been created especially for developers. An automated system creates a developer hierarchy called the Google Desktop Hall of Fame, where programmers can advance based on their gadgets' number and popularity.
The SDK also allows third-party applications to make use of the search facilities provided by Google Desktop Search. For example, the file manager Directory Opus offers integrated Google Desktop Search support.
So, what are you waiting for? Go and install the latest 5 beta version at- http://desktop.google.com


